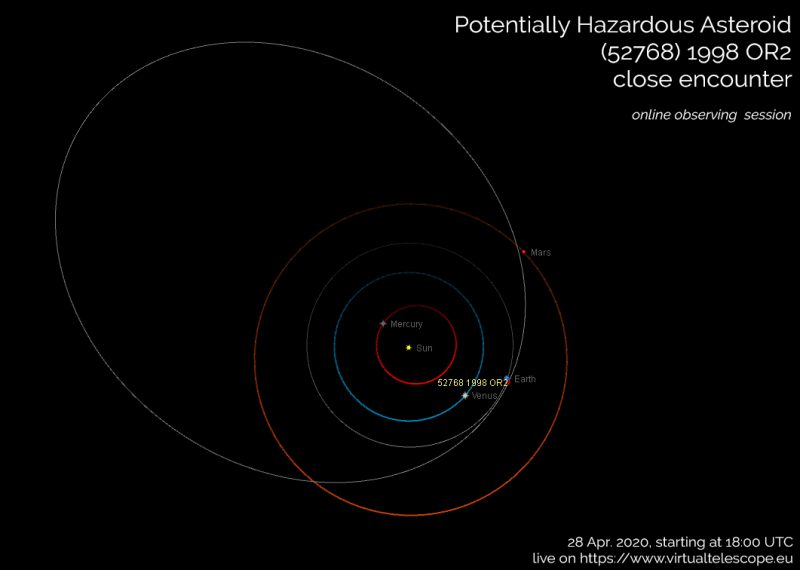
According to NASA, an asteroid, 1998 OR2, which was discovered back in 1998, will approach the Earth’s orbit on April 29, 2020.
After a superficial study of the behavior of a cosmic body, it was assigned to the category of potentially dangerous celestial objects.
Read also: Nikola Tesla Wanted To Create Rings Around The Earth Like Saturn, But Why?
According to rough estimates, its size can vary in the range of 1.8 Km to 4 km. Asteroid makes a complete revolution around the Earth in almost 4 years. Following its trajectory, it periodically approaches the Earth’s orbit.
The distance between the earth and the cosmic body 1998 OR2 will be approximately 6 million kilometers, which is 16 times the distance between Earth and the moon.
Self-moving space objects are commonly called asteroids. Their sizes can be very small on a celestial scale or can exceed the radius of the Earth several times.
One of these objects was the asteroid 1998 OR2. It has its own orbit and frequency of movement. From time to time, these factors reduce it to the earth’s orbit.
Read also: In 2022, An Asteroid 15 Times Stronger Than Hiroshima Bomb Can Hit Earth
Theoretically, the trajectory of an asteroid can change. For this, its collision with another body must occur somewhere in the vast cosmic expanses. The consequences of such an incident are unpredictable.
Another danger that asteroids carry is the difficulty of observing them. They have no gravity, no glow like comets. Rather often, asteroids are detected by accident when they enter the line of sight from Earth. Then, going into outer space, they are lost in pitch darkness.
Astrophysicists do not exclude the possibility of a collision of the Earth with another space object.
NASA scientists saw the approach of the 1998 OR2 as an opportunity to conduct exercises. Their essence is to prevent the collision of the Earth with space objects. The plans were to launch a certain body that would change the trajectory of the asteroid, pushing it away from Earth’s orbit.
The scientists plan to obtain additional data on the asteroid 1998 OR2, including the minimum distance of approach to the Earth. This will allow in future to better predict the behavior of space guests.








