The heart of business process management is automation. Successful businesses must seize every chance to automate monotonous, time-consuming manual operations using available technologies.
Workflow automation streamlines commercial operations like data entry, social media updates, inventory management, and reporting while relieving your staff of tedious and routine tasks. This increases output, as well as lowers expenses, and minimizes human error. Flokzu is a cloud solution for process automation that offers effective business process management examples for your business to deliver better results.
Business process management (BPM) is a systematic management strategy with the goal of enhancing the efficiency and performance of your organization. This method gives the organization the ability to define its processes, plan for their execution, and enhance the quality of the output of the processes and the sequence in which they are carried out.
A business process is a series of interconnected tasks or actions intended to provide a certain good or service for customers. A business process may be defined as any logical set of steps that are consistently performed and provide a specific business outcome for each type of activity. Each activity that is repeatedly performed is an algorithm and is referred to as a business process.
It is worth mentioning that the business process serves other purposes besides obtaining a profit. Business processes include things like recruiting and firing workers, vacation requests, transfers, and other employee-to-employee interactions inside the organization.
Why You Need Business Process Management
Business processes are necessary to generate revenue and grow your company, as well as not to lose your business. This will need extensive analytical effort, including research on the market, your rivals, your customers, and most significantly, your own business.
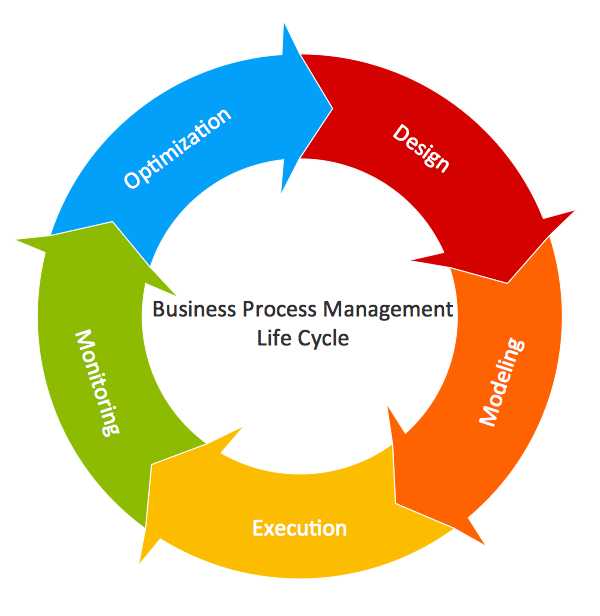
So, profit is the primary objective of a business. There is a certain way to achieve it, and occasionally more than one. Which is the wiser option? Management involves identifying significant intersections along this route as well as means to succeed and control mechanisms.
Business process management uses the following approaches:
– standardization of processes that is thorough, clear, and recorded, as well as the development of a set of standardized processes that may be modified to accommodate varying circumstances;
– continuous process improvement, incorporating daily process measurement, analysis, and modification;
– the use of software and information technologies, such as business process modeling, automation, and optimization based on information technologies.
Types of Business Processes
Business processes are classified into several categories, and business process management covers all of them. Business processes may be divided into three categories:
– Management processes. They are made to organize, track, and evaluate work. Goals may be guaranteed to be attained by production and supporting processes through management processes. Although management processes do not offer value for the customer, they are essential to the smooth and successful functioning of the business. These processes frequently involve budgeting, goal-setting, monitoring, and measuring.
– Production (basic) processes. The business reaches its objectives with them. A product or service is modified during the manufacturing process, adding value for the consumer. Design, manufacture, service providing, installation, and other procedures are all included in the production processes.
– Supporting processes. The proper execution of industrial operations depends on these processes. While they do not offer value for the final customer, they are necessary for the production processes. A few examples of supporting processes include infrastructure management, people management, and procurement processes.
Business Process Management Examples
Business process management systems are now widely used by various businesses. They enable you to organize and manage a wide range of activities that are common in businesses.
Consider a sizable company with numerous workshops and a wide range of equipment. The organization’s manager is required to monitor the equipment and fix various elements of the machinery on a regular basis. Organizing the supply of new equipment, raw materials, and completed items will also take time.
These processes all demand resources and time. Labor productivity suffers greatly in the absence of rules governing the use of repetitive procedures or their automation, and the cost of the produced goods goes up.
Imagine that such a company has deployed one of the business process management systems. The system works together with the corresponding detectors to gather data in real-time while controlling the condition of the equipment. It includes algorithms that, for instance, forecast when a certain mechanism component will be needed to get exchanged.
The labor is not entirely done for the employee by automatic systems, though. It may be set up to handle a variety of company activities and vastly improve worker productivity. Consider how often equipment has to be maintained and repaired.
The management must assign personnel to oversee the condition of the machinery if planning is done manually at the company. Another unit will now be required to handle theoretical calculations. Both demand a lot of time and special consideration.
After automatic business process management systems have been implemented at the company, the manager merely needs to update the system with the relevant information on the mechanisms.
Further, an automated calculation will determine the costs of equipment repair. The system also suggests which equipment should be turned off when a certain unit is being repaired, taking into consideration the interdependence of the various systems.
Besides, in an automated mode, it is possible to handle the provision of essential supplies, the maintenance of production facilities, the number of safety briefings, etc.
The key advantages of implementing business process management are:
• enhancing owner transparency in business;
• cost savings brought on by the replacement or exit of important managers;
• an improvement in managerial effectiveness as a result of the ability to oversee employees’ activities;
• a coordinated flow between structural divisions;
• setting up the necessary conditions for the core automation of business operations.








