A group of American and Chinese geologists believes that there may be “iron snow” in the inner core of the Earth. Studies show that iron “flakes” can fall out of the outer core and settle on the inner core.
Read also: Two Mountains Bigger Than Mt. Everest Found Inside Earth: Does it mean Earth Is Hollow?
Since we cannot see what is happening at a depth of more than 3,000 kilometers, scientists are forced to conduct research in the laboratory.
For this, they use seismic waves that propagate more slowly or faster depending on the structure of the material.
However, this research method yields results that are not consistent with our current models.
For example, it seems that seismic waves propagate more slowly than expected through the inner part of the outer core and faster through the upper part of the inner core, especially in the eastern hemisphere.
Read also: In 2022, An Asteroid 15 Times Stronger Than Hiroshima Bomb Can Hit Earth
Scientists from China and the United States came up with a theory that can explain these obscure anomalies.
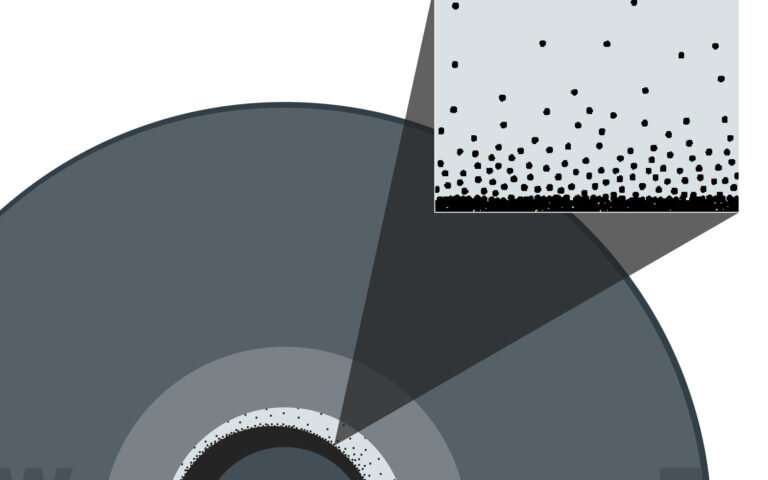
Experiments using materials similar to those in the core suggest that crystallization of molten iron can occur at the bottom of the outer core, which then precipitates on the inner core.
According to the researchers, this substance may have a suspension consistency, which effectively slows down seismic waves.
The layer may be spotty, which makes it thinner in the eastern hemisphere and thicker in the western hemisphere, which may explain why seismic waves propagate there at different speeds.
In addition, this process may explain why the inner core is constantly growing.
If iron snow falls in reality, it can affect many processes on Earth, including how heat and stones move in different areas, and how the Earth’s magnetic field is generated.








